Let’s talk about something most of us tend to brush off sleep apnea. Whether it’s you, your partner, or even your toddler, those nighttime snores and restless nights might be more than just an annoyance. Sleep apnea isn’t just about snoring, it’s a serious condition that can impact your overall health. But don’t worry, we’re here to break it down in a way that makes sense. By the end of this, you’ll know exactly what to look out for and what steps to take.
What Is Sleep Apnea?
you’re sleeping soundly (or so you think), but your breathing keeps stopping and starting throughout the night. Sounds scary, right? That’s exactly what sleep apnea does. It interrupts your breathing, sometimes hundreds of times a night, without you even realizing it. Your body keeps waking you up just enough to restart your breathing but it disrupts your sleep cycle. The result? You wake up feeling exhausted, no matter how long you were in bed.
There are three types of sleep apnea:
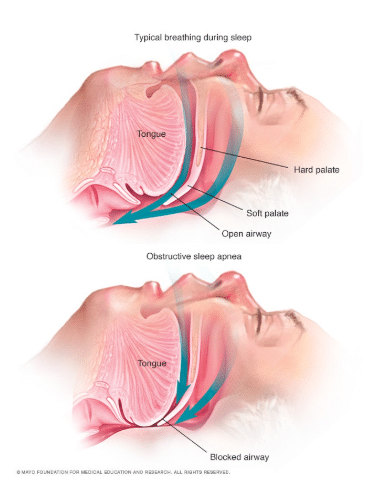
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): The most common type, where the muscles in your throat relax and block your airway.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): A less common type where your brain doesn’t send the right signals to control your breathing.
- Complex Sleep Apnea: A mix of both OSA and CSA.
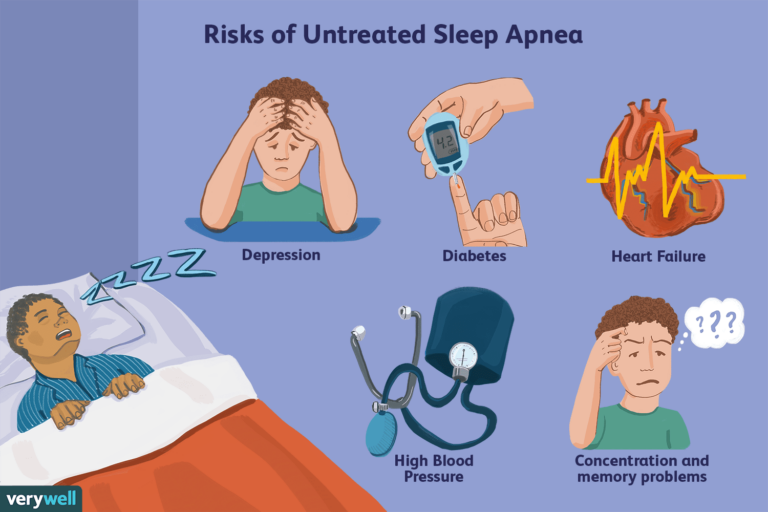
Left untreated, sleep apnea can lead to serious health problems like heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and even stroke. Yikes, right? Let’s dive into the signs so you know when to take action.
Signs and Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
For Adults
If you notice any of these signs, it might be time to have a chat with your doctor:
- Loud snoring: We’re talking loud enough to shake the walls—or your partner’s patience.
- Pauses in breathing: Your partner might notice you stop breathing for a few seconds at a time.
- Gasping or choking during sleep: Ever wake up feeling like you’re fighting for air? That’s a big red flag.
- Morning headaches: Frequent headaches after waking up can point to oxygen deprivation during the night.
- Daytime fatigue: No matter how much you sleep, you’re constantly tired. Falling asleep during meetings? Been there.
- Frequent nighttime trips to the bathroom: Waking up multiple times to pee isn’t normal.
- Dry mouth or sore throat in the morning: Breathing through your mouth all night can leave you feeling parched.
- Mood swings and irritability: Lack of sleep can turn anyone into a grump.
- Memory and concentration issues: Struggling to focus or remember things? It might be more than just stress.
- Decreased libido or sexual dysfunction: Sleep apnea can mess with your hormones, affecting your Intercourse.
For Children
Kids can experience sleep apnea too, but the signs often look a little different. Watch out for:
- Snoring: If your child snores regularly, don’t ignore it.
- Mouth breathing: Both during sleep and while awake.
- Bedwetting: Especially if they’ve already outgrown it.
- Daytime sleepiness: Falling asleep during class or seeming unusually tired.
- Difficulty concentrating: Sleep apnea can mimic ADHD symptoms, affecting their performance at school.
For Toddlers
Sleep apnea in toddlers? Yep, it happens. Here are some telltale signs:
- Restless sleep: Tossing, turning, and trouble staying asleep.
- Sweating heavily at night: This isn’t just because they’re bundled up, it could be a sign of breathing struggles.
- Irritability during the day: A cranky toddler might not just be moody, they might be exhausted.
- Slow growth: If your little one isn’t gaining weight or growing as expected, sleep apnea could be a factor.
Why Sleep Apnea Happens
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
This type happens when the soft tissues in your throat (like your tongue or tonsils) block your airway. Common risk factors include:
- Being overweight.
- A thick neck or narrow airway.
- Smoking or drinking alcohol.
- Family history of sleep apnea.
- Being older or post-menopausal for women.
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA)
Here, the problem lies with your brain, it’s not sending the right signals to your muscles to keep you breathing. Causes include:
- Heart conditions like congestive heart failure.
- Certain medications, like opioids.
- High altitudes.
- Previous strokes.
When to See a Doctor
So, when should you stop brushing off the symptoms and actually see a doctor? If you or a loved one experience:
- Loud snoring that disrupts your sleep or your partner’s.
- Episodes of stopped breathing during the night.
- Extreme daytime fatigue.
- Difficulty managing conditions like high blood pressure or diabetes.
Your doctor might refer you to a sleep specialist, who will likely recommend a sleep study. This test monitors your breathing, oxygen levels, and other vital signs while you sleep, either at a sleep center or in the comfort of your home.
Treatment Options for Sleep Apnea
Let’s talk solutions! The good news is that sleep apnea is treatable.
Lifestyle Changes
- Weight loss: Shedding even 10% of your body weight can make a huge difference.
- Sleeping position: Avoid sleeping on your back, it can worsen OSA. Try a special pillow to stay on your side.
- Avoid alcohol and sedatives: These relax your throat muscles, making things worse.
Medical Devices
- CPAP Machines: The gold standard for treating sleep apnea, these machines deliver pressurized air to keep your airway open. The mask might take some getting used to, but the results are worth it.
- Oral Appliances: These custom-made devices reposition your jaw or tongue to prevent airway collapse.
Surgical Options
- Tonsillectomy or adenoidectomy: Especially common for kids with OSA.
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP): Removes excess tissue from the throat to widen the airway.
- Jaw surgery: Adjusts the position of your jaw to prevent blockages.
FAQs About Sleep Apnea
1. Can sleep apnea go away on its own?
For some people, lifestyle changes like losing weight can significantly improve or even resolve sleep apnea. But for others, ongoing treatment is necessary.
2. Is snoring always a sign of sleep apnea?
Not necessarily. While loud, frequent snoring is a common symptom, not everyone who snores has sleep apnea.
3. Can children outgrow sleep apnea?
Sometimes, yes especially if enlarged tonsils or adenoids are the cause. In other cases, treatment may be needed.
4. Does sleep apnea cause heart problems?
Absolutely. Untreated sleep apnea increases the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
5. Is CPAP the only treatment?
Not at all! While CPAP is highly effective, there are other options like oral appliances, lifestyle changes, and even surgery.
Sleep Apnea Symptoms by Age
| Age Group | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Adults | Snoring, fatigue, morning headaches, dry mouth, irritability |
| Children | Snoring, bedwetting, poor attention, daytime sleepiness |
| Toddlers | Restlessness, slow growth, irritability, night sweating |
Don’t Sleep on Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea might sound scary, but it’s manageable and in many cases, life-changing once treated. If you or a loved one show any signs, don’t wait. Talk to a doctor or sleep specialist.
The sooner you address it, the sooner you can enjoy restful, restorative sleep and the health benefits that come with it.
References
- Mayo Clinic: Sleep Apnea Overview
- Cleveland Clinic: Sleep Apnea Symptoms
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Sleep Apnea Basics