Anxiety is a natural response to stress or danger, something we all experience occasionally. However, for some people, anxiety becomes a persistent and overwhelming issue that interferes with their daily life. When this happens, it is classified as an anxiety disorder a group of mental health conditions characterized by excessive fear or worry. Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health challenges, affecting millions of people worldwide.
This article explores anxiety disorders, their symptoms, types, and treatment options while offering tips for managing anxiety effectively.
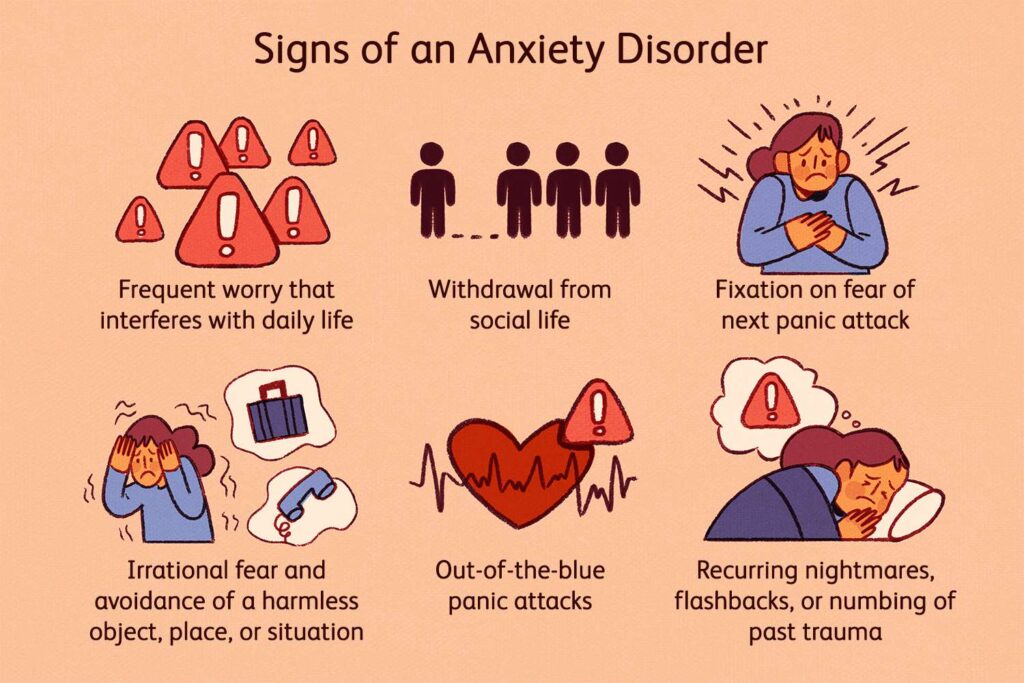
Understanding Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders differ from everyday anxiety in intensity, duration, and impact. While normal anxiety helps us respond to danger or challenges, anxiety disorders involve irrational fears that are disproportionate to the actual situation. These fears are often chronic and can lead to significant distress or impairment.
Table: Types of Anxiety Disorders and Their Key Characteristics
| Type of Anxiety Disorder | Key Characteristics | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) | Persistent and excessive worry about various aspects of daily life, such as work, health, or relationships. | Restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, muscle tension, and sleep disturbances. |
| Social Anxiety Disorder (Social Phobia) | Intense fear of social situations due to fear of embarrassment or judgment by others. | Avoidance of social events, sweating, trembling, nausea, and difficulty speaking in public. |
| Panic Disorder | Recurrent, unexpected panic attacks accompanied by fear of additional attacks or their consequences. | Rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, dizziness, chest pain, and a sense of impending doom. |
| Specific Phobias | Irrational fear of a specific object, situation, or activity, leading to avoidance. | Intense anxiety or panic when exposed to the feared object or situation (e.g., fear of heights or flying). |
| Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) | Intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions) aimed at reducing anxiety. | Excessive handwashing, checking, arranging, or mental rituals to neutralize obsessive thoughts. |
| Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) | Anxiety triggered by experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. | Flashbacks, nightmares, hypervigilance, and avoidance of reminders of the trauma. |
Key Facts About Anxiety Disorders
- Anxiety disorders affect approximately 25% of the population at some point in their lives.
- Another 25% experience less severe anxieties, such as specific fears of spiders or snakes.
- Anxiety disorders often co-occur with depression, creating additional challenges for those affected.
Symptoms of Anxiety Disorders
The primary feature of anxiety disorders is persistent fear or worry that disrupts a person’s ability to function. Symptoms can be both emotional and physical, including:
Emotional Symptoms
- Chronic worry or fear that feels uncontrollable.
- A sense of dread or impending doom.
- Fear of panic attacks or situations that might trigger them.
Physical Symptoms
- Trembling, sweating, or feeling faint.
- Rapid heartbeat or shortness of breath.
- Nausea, dizziness, or choking sensations.
Panic Attacks
A panic attack is a sudden surge of intense fear or discomfort that peaks within minutes. It can occur in response to a situation or seemingly out of nowhere.
Symptoms of a Panic Attack:
- Racing heartbeat.
- Feeling like you’re choking.
- Sweating, trembling, or dizziness.
- A sense of losing control or impending doom.
Although panic attacks are common in anxiety disorders, experiencing one doesn’t necessarily mean someone has an anxiety disorder. Frequent panic attacks, however, can lead to other conditions such as agoraphobia.
Types of Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders encompass a variety of conditions, each with its own characteristics.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) | Chronic worry about everyday things like family, health, or finances. |
| Social Phobia | Fear of being judged or humiliated in social situations, leading to avoidance. |
| Specific Phobias | Irrational fears of specific objects or situations, such as spiders (arachnophobia) or heights. |
| Panic Disorder | Recurring and unexpected panic attacks, with a persistent fear of future attacks. |
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
People with GAD experience constant worry about various aspects of life, such as work, relationships, or health. This worry is excessive, lasting most days for at least six months.
Common Symptoms:
- Difficulty concentrating or relaxing.
- Fatigue and restlessness.
- Trouble controlling worry despite recognizing it as irrational.
Social Phobia
Also known as social anxiety disorder, this condition involves an intense fear of being embarrassed, judged, or humiliated in public.
Common Triggers:
- Public speaking.
- Using public facilities, such as restrooms or cafeterias.
- Attending social gatherings.
People with social phobia often avoid situations that make them anxious, which can lead to isolation and difficulty maintaining relationships.
Specific Phobias
Specific phobias involve extreme fear of a particular object or situation, such as:
- Heights (acrophobia).
- Enclosed spaces (claustrophobia).
- Animals (e.g., dogs, spiders).
Although sufferers recognize that their fear is irrational, the intense anxiety they feel leads to avoidance behaviors that interfere with daily life.
Panic Disorder
Panic disorder is characterized by frequent, debilitating panic attacks. Unlike a specific phobia, panic attacks in this condition may occur spontaneously, without an identifiable trigger.
Diagnosis Criteria:
- At least four panic attacks per month over an extended period.
- Persistent fear of having another attack.
The Impact of Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders can affect many aspects of life, including:
- Social Isolation: People may avoid social interactions due to fear of judgment or embarrassment.
- Work and Education: Difficulty concentrating or managing anxiety can interfere with job performance or academic success.
- Relationships: Constant worry or irritability may strain relationships with family, friends, and colleagues.
- Mental Health: Anxiety often co-occurs with depression, increasing the risk of self-harm or suicide.
Treatment for Anxiety Disorders
The good news is that anxiety disorders are highly treatable with the right combination of therapy, lifestyle changes, and medication.
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is one of the most effective treatments for anxiety disorders. It helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns that contribute to anxiety.
2. Exposure Therapy
This method gradually exposes individuals to anxiety-provoking situations in a controlled way. By confronting fears step-by-step, people can learn to manage their anxiety more effectively.
3. Relaxation Techniques
Practices such as deep breathing, mindfulness, and progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce physical symptoms of anxiety.
4. Medication
For severe anxiety, medications such as antidepressants (e.g., SSRIs) or benzodiazepines may be prescribed. Medications are often used in conjunction with therapy.
5. Lifestyle Changes
- Regular exercise can release endorphins, improving mood.
- Maintaining a healthy diet supports overall well-being.
- Establishing a routine promotes a sense of stability and control.
Tips for Managing Anxiety
| Tip | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Practice Mindfulness | Helps focus on the present moment and reduces overthinking. |
| Create a Calm Space | Having a clutter-free, soothing environment can ease anxiety. |
| Limit Stimulants | Reducing caffeine and alcohol intake can prevent physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat. |
| Stay Active | Physical activity boosts mood and helps release tension. |
| Seek Social Support | Talking to trusted friends or joining support groups reduces feelings of isolation. |
The Path to Recovery
Anxiety disorders may feel overwhelming, but recovery is possible with the right support and treatment. A combination of therapy, medication, and self-care practices can help individuals regain control of their lives.
Authentic US Sources for Anxiety Information
For reliable information on anxiety disorders and their treatment, explore these trusted sources:
- National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH): www.nimh.nih.gov
- Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA): www.adaa.org
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA): www.samhsa.gov
- Mayo Clinic: www.mayoclinic.org
- American Psychological Association (APA): www.apa.org
Conclusion
Anxiety disorders are common but highly manageable with proper treatment and support. By understanding the symptoms, types, and treatment options, you can take the first step toward recovery. Remember, you’re not alone, and help is always available. Whether through therapy, medication, or lifestyle changes, there is hope for overcoming anxiety and living a fulfilling life.


